Heart and it's function | quick revision for NEET
 |
| Photo By Ai |
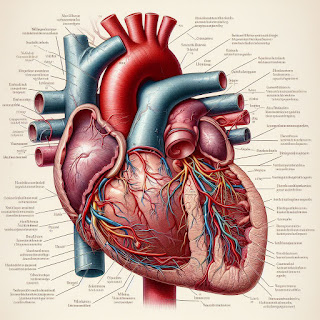
- Heart Structure:
- Four-chambered organ located in the chest cavity.
- Made of cardiac muscle tissue.
- Divided into the right and left sides by septum.
- Heart Chambers:
- Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Right Ventricle: Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via pulmonary veins.
- Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the aorta.
- Heart Valves:
- Tricuspid Valve: Between right atrium and right ventricle.
- Pulmonary Valve: Between right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- Mitral Valve (Bicuspid): Between left atrium and left ventricle.
- Aortic Valve: Between left ventricle and aorta.
- Heart Circulation:
- Systemic Circulation: Oxygen-rich blood pumped from left ventricle to body tissues via arteries, returns as deoxygenated blood through veins to right atrium.
- Pulmonary Circulation: Deoxygenated blood pumped from right ventricle to lungs via pulmonary arteries, returns as oxygenated blood through pulmonary veins to left atrium.
- Heart Functions:
- Pumping Action: Contracts rhythmically to circulate blood throughout the body.
- Oxygenation: Receives oxygen-poor blood from the body, pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation, and receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs, pumping it to the body.
- Regulation: Maintains blood pressure and circulation by adjusting heart rate and contractility.
- Endocrine Function: Produces hormones such as atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) to regulate blood volume and pressure.
- Heartbeat Regulation:
- Controlled by electrical impulses generated by the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart's natural pacemaker.
- Impulses travel through the atria, causing them to contract, then to the atrioventricular (AV) node, and finally to the ventricles, causing them to contract.
- Autonomic nervous system, hormones, and other factors influence heart rate and rhythm.
- Heart Health:
- Regular exercise, balanced diet, and lifestyle choices are crucial for heart health.
- Conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and valve disorders can impact heart function.
- Medical interventions like medications, surgeries, and lifestyle changes are used to manage heart conditions and maintain cardiovascular health.